●Japanese / ●English
-Distributed Energy System with Hydrogen Storage-
Social Implementation Research Group
About This Technology
About This Technology
Background Issue
Renewable energy using solar power and wind power is an unstable power source. Therefore, for example, even if a large amount of power can be generated, the power output may suppress when the power sources are connected to the grid directly. At present, the power output frequently suppresses in Kyushu area, Japan. This suppression is expected to spread worldwide.
System Features
The key technology of this system is the energy management protocol. In this technology, the surplus energy is stored in hydrogen so that the stored energy can be used on demand. This system can be used as an independent power source. It will be possible to use it as an emergency power source when it is needed. Furthermore, since this technology has high flexibility and scalability, we will fabricate a distributed energy system connecting multiple devices with less loss by learning power generation and consumption trends with AI. In addition, this technology is suitable for the areas where it is difficult to deliver grid power.
❶ Electrochemical system based on Polymer Electrolyte Electrolytic Cell (PEEC) and polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell (PEFC)
- Since the PEEC and PEFC are operated under normal temperature and normal pressure,do not use alkaline, and the devices are suitable for ON/OFF operations, the system can be installed anywhere, and easy to maintain.
- Since the energy efficiency of the electrochemical process is similar even the system size changes to small, the system is possible to fabricate with multiple mass-produced unit systems (e.g. 5, 10, 50KW).
- Energy efficiency can be further improved by combining with thermal management.
❷ Connecting power generations, storages, and power loads to the DC bus line(main power line), and controlling storage/power generation by raising/lowering the voltage level of the bus line (RIKEN experimental system : 340V±5V).
- The system has unique energy management protocol. The voltage level of the DC bus line is controlled by the energy flow to/from the storage device(s) which has fast response to the energy demand of the system input/output.
- Since operation is controlled by the voltage level of the DC bus line autonomously, the distributed energy system simply controls the parameters of the system when it is needed. –> Simple configuration, simple control, cost reduction
- Since each device is connected to the DC bus line, it is easy to expand and contract the devices as well as connect and separate the systems. –> High flexibility and scalability as a distributed system, easy to handle changes
❸ Hybrid energy storage system combining secondary battery and hydrogen storage
- A power supply design that combines the merits of Main Voltage Controller(s) (MVC) that supports high-speed power fluctuations and Sub Voltage Controller(s) (SVC) that is low-speed but low-cost and large-capacity storage(s).
- MVC is secondary batteries (e.g. LiB), and SVC is water electrolyzers (EC), hydrogen storage (H2Storage), and fuel cells (FC), for example.
Basic configuration of RIKEN distributed energy system with hydrogen storage
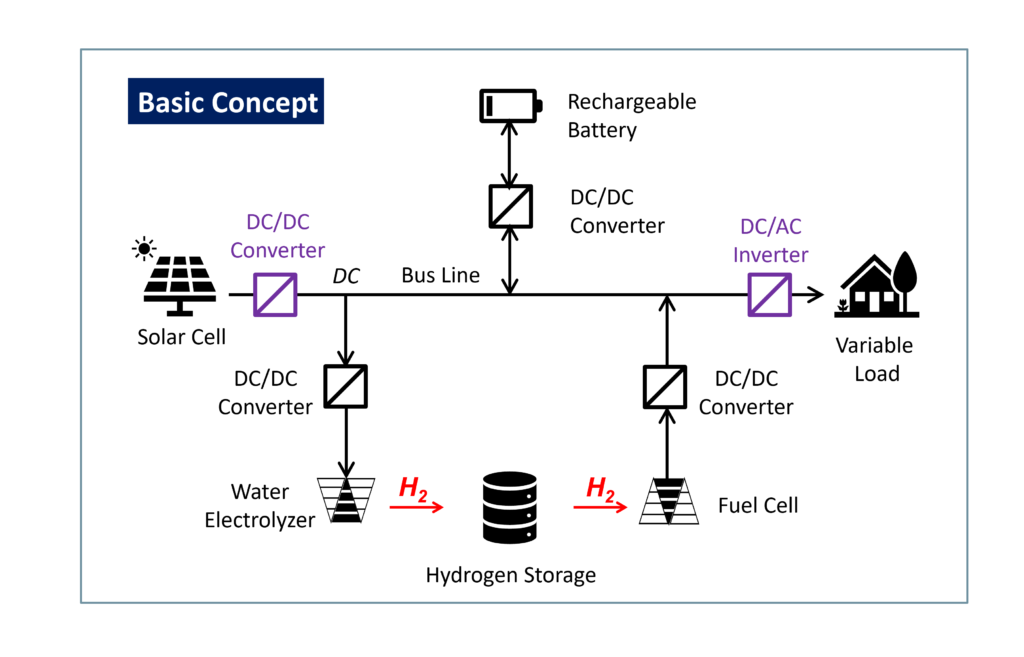
Target of RIKEN distributed energy system with hydrogen storage
Experimental Hydrogen System
Currently, we have installed two experimental hydrogen systems, “100W” and “2kW”, on the RIKEN Wako Campus.
100W compact hydrogen system
・Gas related equipment (500 x 400 x 420mm)
Water electrolyzer (including water supply system, EC):
100W
Fuel cell (including hydrogen supply control, FC): 100W
Hydrogen tank (H2Storage): Maximum 0.7MPa, 4L
*Specifications may change in the future.
*Prototype equipment aiming for miniaturization and
low cost
・Control unit (600 x 600 x 580mm)
Gas-related equipment control
DC power supply
DC power load
*Solar cells (PV) and DC/AC inverters are under
consideration for expansion

2kW unit hydrogen system
・Aiming to achieve multi-input, multi-storage, and multi-output
・Solar battery (PV): 1.3 kW
Water electrolyzer (EC): 1.5kW
Fuel cell (FC): 2.0 kW
Hydrogen storage (H2Storage): 2m3, <0.7MPa
DC/AC inverter: 0.5kW
・Renewable energy storage system capable of Grid
linkage and self-sustaining operation

Published Patents, Academic Papers, Reviews
- 直流バス制御システム:
1) 特願JP2019-555345,AU,CN,EP,KR,US
2) 特願JP2022-512265
3) 特願JP2022-532381,US
4) 特願JP2022/036033
5) 特願JP2022/045490 - D. Yamashita, et al., “Distributed control of a user-on-demand renewable-energy power-source system using battery and hydrogen hybrid energy-storage devices,” Int.J.HydrogenEnergy, vol.44, pp. 27542-27552, 2019.
- 藤井 他, “ユーザー・オン・デマンド再生可能エネルギー供給システム,” クリーンエネルギー, vol.28, pp.25-33, 2019.
- 藤井 他, “太陽電池からの高効率水素貯蔵と, 水素貯蔵を利用した小型エネルギーマネジメントの実際,” えねるみくす, vol.98(3),pp.240-247, 2019.
- 小川 他, “太陽光を利用した植物工場の低コスト化,” J.JSES, vol.45(4), pp.10-15, 2019.
- 小池 他, “ユーザーオンデマンドを実現する自律型再生可能エネルギーシステム” ケミカルエンジニヤリング, pp.811-816, 2019.
- 藤井 他, “ユーザーオンデマンド再生可能エネルギー供給システム,” 化学工業, vol.71, pp.606-612, 2020.
- 藤井 他, “再生可能エネルギーを利用したエネルギー供給システムの制御方法,” クリーンテクノロジー, vol.30, pp.41-46, 2020.
- 藤井 他, “自然エネルギー源を利用した水素貯蔵小型エネルギーシステムの簡易的な地域最適化指針,” J.Jpn.Inst.Energy,vol.100(6), pp.45-54, 2021.
- 半田 他, “分散型水素エネルギーシステムの展望とその要素技術の開発,” スマートグリッド, vol.63(10), pp.9-13, 2022.
- K. Tsuno, et al., “User-on-demand Renewable Energy Supply System Using Modified DC-bus Signaling,” IFAC Papers Online 56-2(2023) 9098-9103.
- S. Wada, et al., “Self-Controlled Electric Power Supply System from Solar Cells Using Hydrogen Storage,” 2023 AlChE Annual Meeting.
Inquiries about This Technology
Riken Innovation Co., Ltd.
” Distributed Energy System with Hydrogen Storage ” Social Implementation Research Group Secretariat
Email suisobunsan@innovation-riken.jp
© Distributed Energy System with Hydrogen Storage Socail Implementation Research Group.


